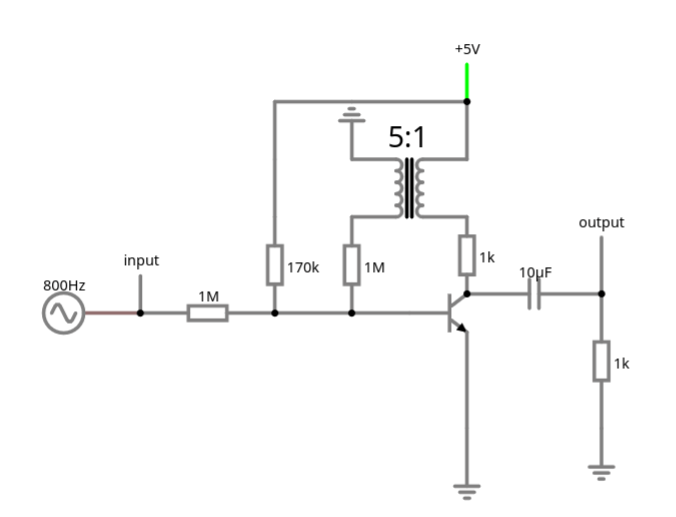
Many old AM receiver circuits use positive feedback (routing some of the already amplified output signal back into the amplifier's input) for more gain. These circuits (eg. the reflex receiver [REF]) are fascinating designs which, although not overly complex, aren't easily understood. Starting with an existing circuit design, I tried to isolate the feedback loop … Continue reading 1-Transistor feedback amplifier
Tag: electronics
Comparing the efficiency of DC voltage boost circuits
Overview & disclaimers This post compares the power efficiency of some voltage boosting circuits. The circuits discussed here are: Buck converter Parallel buck converter Serial buck converter Pulsed transformer Joule thief Honorary mentions What we're doing here is neither complete nor scientific and aspires to more than it delivers. Comparison base line The generic version … Continue reading Comparing the efficiency of DC voltage boost circuits
Simplified double push-pull amplifier
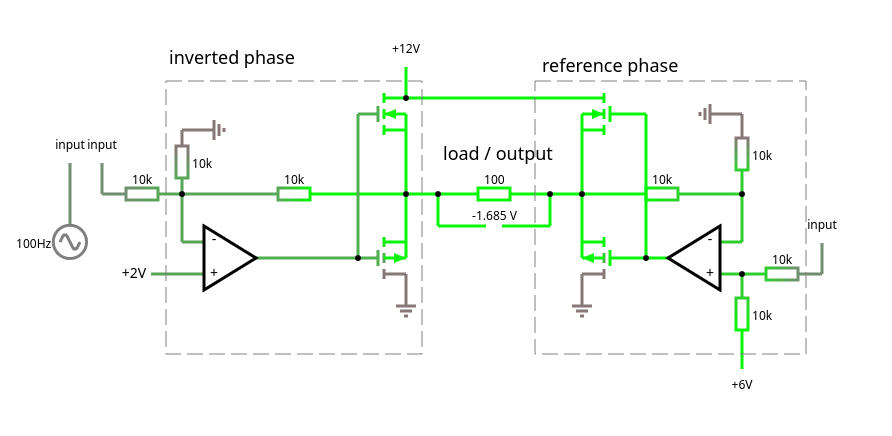
There exists a simpler design for the double push-pull amplifier with cross-over compensation [DPP]. A quick recap of the previous design: the input signal is divided into a reference phase and an inverted phase, each phases are amplified separately and drive two push-pull amplifiers [PPA] respectively. What happened so far: while in absolute terms simple, … Continue reading Simplified double push-pull amplifier
Double push-pull amplifier with cross over compensation
Push-pull amplifiers [1] are great for driving heavy loads because they divide work among two transistors and produce a centred output signal that can freely move up or down around the centre. Simple push-pull amplifier When powering the amplifier with a single power source (eg. a 12V battery), then the output signal oscillates around half … Continue reading Double push-pull amplifier with cross over compensation
Transistor Common Base Configuration – a Hidden Champion
The transistor common base configuration is just as simple as the other two (common collector, common emitter) configurations, but far less known and used - which is a regrettable mistake, because it is absolutely awesome and has little-known characteristics which we'll look into right away! Common base configuration Operating principle At first look, the common … Continue reading Transistor Common Base Configuration – a Hidden Champion